Partial Orders
Given a partial order ![]() on a set
on a set ![]() :
:
An element ![]() is maximal if
is maximal if
An element ![]() is minimal if
is minimal if
An element ![]() is a greatest element if
is a greatest element if
An element ![]() is a least element if
is a least element if
Let ![]() .
.
An element ![]() is a lower bound of
is a lower bound of ![]() if
if
An element ![]() is a greatest lower bound (glb) of
is a greatest lower bound (glb) of ![]() if
if ![]() is a
lower bound of
is a
lower bound of ![]() , and for every lower bound
, and for every lower bound ![]() of
of ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Let ![]() .
.
An element ![]() is a upper bound of
is a upper bound of ![]() if
if
An element ![]() is a least upper bound (lub) of
is a least upper bound (lub) of ![]() if
if ![]() is an
upper bound of
is an
upper bound of ![]() , and for every upper bound
, and for every upper bound ![]() of
of ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Example: project planning.
| Code | Activity | Depends on: |
| A | Rent concert hall | B |
| B | Get sponsors | - |
| C | Print programs | D,A,J |
| D | Get program ads | E |
| E | Plan advertising | B |
| F | Print tickets | G |
| G | Set ticket prices | B |
| H | Advertise | E |
| I | Sell tickets | F |
| J | Get program material | - |
| K | Hold concert | G,C,I |
A partition of a set ![]() is a collection of
is a collection of ![]() sets
sets ![]() (
(![]() ) so that:
) so that:
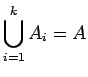 , and
, and
Each subset ![]() is called a block of the partition.
is called a block of the partition.
An equivalence relation ![]() on a set
on a set ![]() partitions the set into
equivalence classes.
partitions the set into
equivalence classes.
An equivalence class is a subset of ![]() so that every pair of elements
from the class is in the relation, while any pair of an element in the
class and an element outside the class is not in the relation.
so that every pair of elements
from the class is in the relation, while any pair of an element in the
class and an element outside the class is not in the relation.
Every element in ![]() is in exactly one of the equivalence classes.
is in exactly one of the equivalence classes.
Notation: ![]() denotes the equivalence class of which
denotes the equivalence class of which ![]() is a
member. Note that
is a
member. Note that ![]() if and only if
if and only if ![]() .
.
Example:
Let ![]() be the relation on the set
be the relation on the set
![]() where
where ![]() if
if
![]() and
and ![]() , divided by 5, have the same remainder.
, divided by 5, have the same remainder.
Equivalence classes:
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() .
.