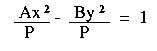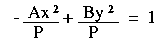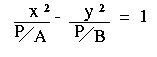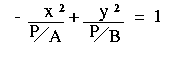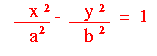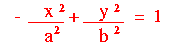| Let's review how we arrived at the standard equation of a hyperbola centred at the origin. |
Opening Direction | left and right | up and down | |
| Graphs |
|
|
| Begin with the equations: | Ax2 - By2 = P
where A, B and P are positive real numbers.* |
-Ax2 + By2 = P
where A, B and P are positive real numbers.* |
| *Note that on the previous page A and B did not always denote positive numbers. We make this distinction here to emphasise the differences between the two equations. Now we have that -A < 0 and -B < 0. |
| Divide both equations by P: | 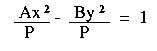 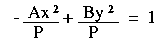 | |
| Rewrite the equations: | 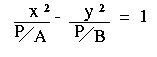 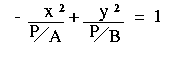 | |
In both cases P/A and P/B are always positive values. This means that: - We can find a real number a such that P/A = a2
- We can find a real number b such that P/B = b2.
|
| Make the substitutions P/A = a2 and P/B = b2 to arrive at the standard equations: | 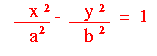 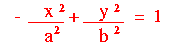 | |
| Information about the graph: |
- The centre of the hyperbola is (0, 0)
- The horizontal axis of symmetry is the x-axis; the vertical axis of symmetry is the y-axis.
- The vertices are located on the x-axis at (a, 0) and (-a, 0)
- a and b both affect the slope of the asymptotes.
| - The centre of the hyperbola is (0, 0)
- The horizontal axis of symmetry is the x-axis; the vertical axis of symmetry is the y-axis.
- The vertices are located on the y-axis at (0, b) and (0, -b).
- a and b both affect the slope of the asymptotes.
|