| After completing this module you will be able to: |
- complete the square algebraically.
|
- describe that an axis of symmetry is a line that divides a geometric figure into two symmetrical parts.
|
- describe or show the number of axes of symmetry a geometric figure has and where these axes of symmetry are located.
|
- describe that a quadratic function in one variable is defined by the equation of the form f(x) = ax2 + bx + c or f(y) = ay2 + by + c where a, b and c are constants and a
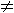 0. 0.
|
- describe or show that the graph of a quadratic function is a parabola.
|
- sketch the graph of a quadratic function by using the equation y = ax2 + bx + c or x = ay2 + by + c to find information about the parabola's opening direction, width, x-intercepts, y-intercepts, axis of symmetry, and vertex coordinates.
|
- sketch the graph or write the equation of a parabola by transforming the graph of the parabola defined by y = ax2 or x = ay2.
|
- write the equation of a line given the coordinates of two points that lie on the line or the coordinates of one point that lies on the line and the slope of the line.
|
- write the equation of a line in slope-intercept form.
|
- sketch the graph of a line given the coordinates of two points that lie on the line, the coordinates of one point that lies on on the line and the slope of the line, or the slope-intercept equation of a line.
|
- describe the ways in which the graph of two linear equations can intersect.
|
- solve a linear-linear system of equations graphically and algebraically.
- check the solutions of a linear system of equations by substituting the solutions of the system into the original equations.
|
|