| Page 2 | PRELIMINARIES Menu | MAIN MENU |
An axis of symmetry is a line that divides a geometric figure into two symmetrical parts.
| These two parts are mirror images or reflections of each other.
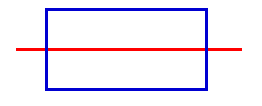
| In Figure 1, the rectangle has a horizontal axis of symmetry. Again notice how the red horizontal line divides the rectangle into two parts that are mirror images or reflections of each other.
| 
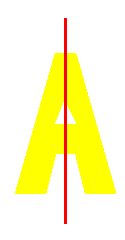
In Figure 2, the letter A has a vertical axis of symmetry. You can see that the vertical red line divides the letter A into two parts that are mirror images or reflections of each other.
| 
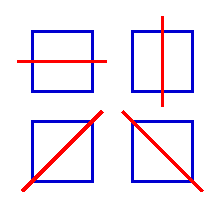
Some geometric shapes have more than one axis of symmetry. For example, a square has 4 axes of symmetry. See Figure 3.
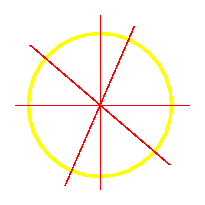
| In Figure 1 above, just a horizontal axis of symmetry is shown. Is there another axis of symmetry? A circle is also an example of a geometric figure that has more than one axis of symmetry. In fact, a circle has infinitly many axes of symmetry. That is, there are infinitely many lines that divide a circle into two symmetrical parts. Figure 4 shows a few of these axes.
| 
Use the figures in the question box to check your understanding of axes of symmetry.
| | |||||||